100 Essential Website Definitions and Web Terms You Must Know

Whether you’re considering building your first website or you’re a more experienced web developer, understanding the essential website definitions will help you work more effectively. This is a jargon-busting list that will provide simple explanations of web development, search engine marketing, and web analytics terminology.
We’ve created four infographics with the 10 most important definitions from each section. Please save the images and share them with friends and colleagues so that you can all have these useful website definitions on hand when you need them most.
Here’s an outline of the article, please feel free to skip ahead to the section that will help you the most:
10 website builder definitions
30 technology and web development terms
30 SEO website definitions
30 analytical website definitions
Website builder definitions
We’re going to start with what we know best and provide you with our top 10 website builder definitions to help those of you who are thinking about using Wix, Squarespace, Shopify, or another leading brand to build your first website. The following website definitions will help you get off to a great start.

Artificial Design Intelligence
Artificial design intelligence uses an algorithm and machine learning to create bespoke website templates with a personalized design based on answers to simple questions and information about your style preferences.
Blog
A blog is a regularly updated web page that features articles or blog posts, usually focused on a niche topic or industry. A blog post can include text, images, or videos. Blogs can help with increasing your website traffic.
DIY Website Builder
A ‘DIY website builder’ refers to a platform that allows users to create, design, and publish a website without needing to use code or a hosting platform.
Drag & Drop
Drag and Drop is a tool available on lots of website builders that allows users to click on elements (text, images, content boxes) on a web page and move them to a new location.
Mobile Optimization
Most website builders will automatically optimize web pages and content for mobiles. This means that web pages and content can automatically adjust to smaller mobile device screens to give mobile visitors a good user experience.
Mobile View
To help with mobile optimization, website builders offer a mobile view so that users can check that any design changes made to web pages look good on mobile screen sizes too.
Online Store
Online stores are websites with added functionalities that allow visitors to shop for products and services over the internet and make payments online.
Web Applications/Third-party Plugins
Web applications or third-party plugins refer to software that can be added to your website to provide additional functionalities that the website builder doesn’t support. For example, you can find plugins that will allow you to add a search bar to your website, add forms to collect email addresses, set up push notifications, and much more. On most website builder platforms with app stores, there is a plugin for everything you can think of.
Website Template
A website template is a pre-designed website framework that users can personalize to their tastes. It means instead of having to create every element of a website from scratch, users can plug in their text, images, and other content to the existing framework. This is a big part of why building a website on a website builder is so quick.
WYSIWYG Web Editor
A WYSIWYG (what you see is what you get) web editor is a web development program that allows developers to edit web pages and content in a form that looks the same as it would on the live web page. This is an evolution from the backend/frontend model where developers would have to publish their web pages to the live website before they could see how their edits had affected the design of the page.
Technology & web development terms
The following 30 website definitions explain some of the more advanced technology and elements involved in making a website. By the time you get to the end of the list, you’ll know the difference between a CDN, CMS, and CSS as well as lots more useful website definitions.
APIs
API stands for Application Programming Interface. It’s a piece of software that acts as the connection between computers, servers, or computer programs, allowing them to talk to each other or swap data. The API then converts and presents that data to you in an accessible format. For example, your favorite messaging app is an API. It sends your messages (data) to a server across the internet, the server interprets the data and sends it across the internet to your friend’s phone, the API on your friend’s phone then presents them the data in the form of a message.
Backend
The backend in web development refers to the code that sits behind a website that allows it to operate. The backend is only accessible to developers and can’t be seen by regular web visitors. It usually consists of one or more coding languages and back-end applications are used to support the frontend. Please see the frontend definition for more information.
Caching
A cache is a temporary storage area used to store data so that when the data is requested again in the future, it can be delivered quicker. It’s used to speed up the loading times of web pages by having elements that take longer to load stored locally on the user’s device. For example, javascript files, stylesheets, and fonts from websites that you use regularly will be stored in your cache memory.
CDN
CDN stands for Content Delivery Network. It describes a network of servers or data centers that are located around the globe. They are used to store content data and speed up website loading times by reducing the physical distance between the user and the server. So, the data reachers the end-user quicker when using a CDN.
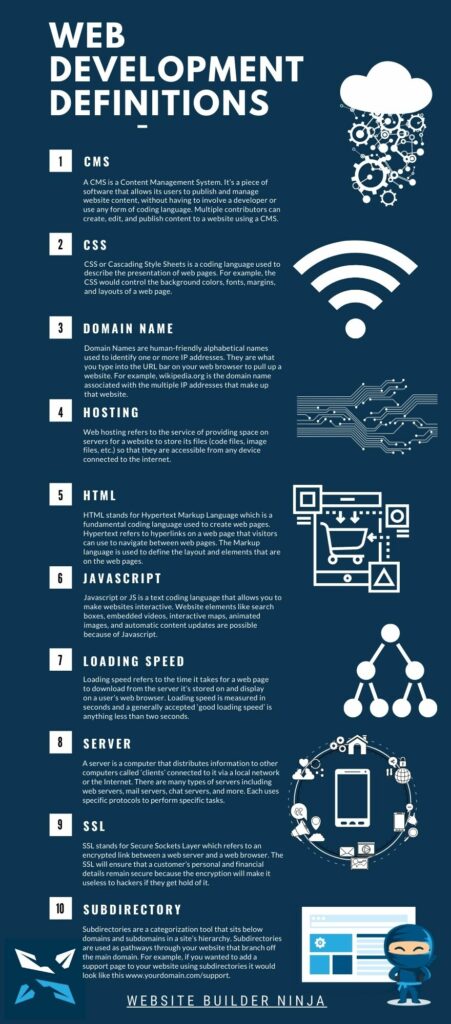
CMS
A CMS is a Content Management System. It’s a piece of software that allows its users to publish and manage website content, without having to involve a developer or use any form of coding language. Multiple contributors can create, edit, and publish content to a website using a CMS. WordPress, Drupal, Joomla, and Magento are the Internet’s most used and most famous content management systems.
Cookie
Cookies are used to improve your browsing experience by saving things like usernames and passwords, as well as to identify individual users. A cookie is a text file that stores a small amount of data. The server creates a cookie with a unique ID for your computer when you connect with it.
CRMs
CRM stands for Customer Relationship Management and refers to a process or software system that helps businesses to manage and analyze data from interactions with customers. It’s used to build better relationships with customers from data insights. For example, a company might find out that one of their products is being commonly damaged during delivery by analyzing the customer complaints data collected by the CRM.
CSS
CSS or Cascading Style Sheets is a coding language used to describe the presentation of web pages. For example, the CSS would control the background colors, fonts, margins, and layouts of a web page.
CSS Attribute
CSS Attributes are used to select and edit (or style) a group of HTML elements with similar attributes. For example, you could use CSS Attributes to change the background color of all your web pages to blue.
DNS
DNS stands for Domain Name System which is the internets system for pairing alphabetic names (domain names like www.yourbusiness.com) with Internet Protocol (IP) addresses that are associated with every website. It helps humans get around the internet easily by allowing us to search with user-friendly names rather than IP addresses that look like this > 192.154. 2.98.
Domain Name
Domain Names are human-friendly alphabetical names used to identify one or more IP addresses. They are what you type into the URL bar on your web browser to pull up a website. For example, wikipedia.org is the domain name associated with the multiple IP addresses that make up that website.
Favicon
A favicon is a small 16×16 pixel icon used to represent a website in web browser tabs. If you look up to your open tabs on your web browser, you will see each tab has a small square icon which is the favicon.
Frontend
Frontend refers to a type of web development that converts coding languages like javascript, HTML, and CSS into a graphical interface. It transforms the code into something web visitors can use and engage with easily. A backend developer focuses on the behind-the-scenes stuff, whereas a frontend developer is responsible for the parts of a website that visitors see and use. For example, menus, forms, galleries, images, and widgets would be classed as frontend development.
Hosting
Web hosting refers to the service of providing space on servers for a website to store its files (code files, image files, etc.) so that they are accessible from any device connected to the internet.
HTML
HTML stands for Hypertext Markup Language which is a fundamental coding language used to create web pages. Hypertext refers to hyperlinks that may be included on a web page that visitors can use to navigate between web pages. The Markup language is used to define the layout and elements that are on the web pages.
IP Address
An IP or Internet Protocol address is a unique numerical code or name linked with every device and website connected to the Internet. IP addresses are an integral part of how data is sent across the internet.
Javascript
Javascript or JS is a text coding language that allows you to make websites interactive. Website elements like search boxes, embedded videos, interactive maps, animated images, and automatic content updates are possible because of Javascript.
Loading Speed
Loading speed refers to the time it takes for a web page to download from the server it’s stored on and display on a user’s web browser. Loading speed is measured in seconds and a generally accepted ‘good loading speed’ is anything less than two seconds.
Margin
Margin in terms of web development refers to the space surrounding the elements or content located on web pages.
Padding
Padding in terms of web development refers to the space between the inside of the border and the image or text located on a web page.
PHP
PHP stands for Hypertext Preprocessor which is an open-source coding language used for web development. It’s embedded within HTML code and is used to communicate with servers. It’s PHP’s job to speak to servers and HTML’s job to speak to programs and devices. So, it facilitates the transfer of data from servers to other computers and software on the network.
Server
A server is a computer that distributes information to other computers called ‘clients’ connected to it via a local network or the Internet. There are many types of servers including web servers, mail servers, chat servers, and more. Each uses specific protocols to perform specific tasks.
SSL
SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer which refers to an encrypted link between a web server and a web browser. It’s an essential security protocol for all websites, especially online stores that accept online payments. The SSL will ensure that a customer’s personal and financial details remain secure because the encryption will make it useless to hackers if they get hold of it.
Subdomain
A subdomain is an additional part of your domain name that is used to categorize sections of your website. It’s possible to have as many subdomains as necessary to categorize each section of your website. For example, if you wanted to add a subdomain for the support section of your website it would change from www.yourdomain.com to www.support.yourdomain.com.
Subdirectory
Subdirectories are another categorization tool that sits below domains and subdomains in a site’s hierarchy. Subdirectories are used as pathways through your website that branch off the main domain. For example, if you wanted to add a support page to your website using subdirectories it would look like this www.yourdomain.com/support.
TTFB
TTFB stands for Time to First Byte and refers to the time it takes for the first byte of data to be received from the web server by the web browsers. TTFB is measured in milliseconds (ms). Generally, a good TTFB time is anything under 200ms while 300-500ms is deemed acceptable.
TTL
TTL stands for Time to Live and is a protocol that’s designed to limit the amount of time that data is stored in a network or cache memory. It’s like an expiry date for data that ensures servers and networks aren’t filled with junk data that no one is using.
VPN
VPN is a three-letter acronym for Virtual Private Network. VPNs allow users to send and receive encrypted data over a public network. So, it creates a private network when connected to a public network to ensure that any data sent from your device to servers during this time is protected.
WAF
WAF or Web Application Firewall is a security application that filters, monitors, and blocks any malicious or unauthorized traffic or data traveling to or from a website or web app.
2FA
2FA or Two-Factor Authentication is used to help protect user access to websites or apps by requiring users to present two forms of evidence before they are granted access. The most common 2FA process involves users inputting a username, password, and one-time code sent via email or text message.
SEO website definitions
If you’re dedicated to building a reliable, relevant, and cheap audience for your website, then getting your head around SEO will help you to do this. This list includes a mixture of basic, technical, and advanced SEO website definitions.

Alt-text
Alt-text or alternative-text is a short text description of an image used to describe the image when the visual content cannot be viewed for some reason. For example, if you’re a search bot, a visually impaired user, or if the web page cannot be fully downloaded.
Blacklisting
Blacklisting is when search engines remove a website from its index which means that the website and its pages cannot show up in search engine results pages. This stops search traffic from reaching the website. Some reasons for blacklisting include duplicate content, keyword stuffing, and too many spammy inbound links. For more detail on blacklisting see this article.
Black-Hat
Black-hat SEO describes a set of practices that are used to improve a website’s search rankings by means that violate search engine policies. Black-hat SEO techniques include keyword stuffing, invisible text, and page swapping. If search engines detect that a website is engaging in black-hat SEO, it is likely to blacklist the site and remove it from its index.
Broken-Link
A broken link is a redundant hyperlink that’s live on a web page. Common causes of broken links are that the linked resource has moved to a new URL or the address has become permanently unavailable due to a website being shut down. Web visitors that click broken links will see a 404-page error.
Canonical URL/Tags
A Canonical tag is an HTML code snippet that signals to search engines that a URL is the main page or original source of content that might be duplicated elsewhere. It helps web developers prevent duplicate content issues when they plan to use the same content across several pages of their website or if they wish to syndicate content to other websites.
Crawling
Crawling refers to the process of search engine ‘crawlers’, ‘spiders’ or ‘bots’ scouring the entire internet to find web pages to index so that they can appear in search engine results pages.
Domain Authority
Domain authority was developed by MOZ as a tool to measure the success of a website’s search engine ranking power. A high domain authority would suggest that a website has high-quality content that’s relevant to a specific industry or niche topic. Domain authority doesn’t directly affect ranking ability but it measures how well a site has optimized for search engines.
Dynamic Content
Dynamic content describes any form of content that adapts a visitor’s data or in-session behavior to create personalized content that’s unique to individual users. Certain types of dynamic content like product recommendation engines can change on every session based on what the user added to their cart in their previous session. A basic example of dynamic content would be an email that inputs each recipient’s first name automatically.
Follow/Nofollow
Follow and Nofollow links are HTML tags used to signal to search engine crawlers whether to give or reject ‘link juice’ or SEO points to a hyperlink included on a web page. Follow links will improve the page rank of the linked page, whereas Nofollow links will not improve the page rank of the linked page.
Friendly URLs
A friendly URL is an easy-to-read web address that helps visitors and search engine crawlers understand what a web page is about quickly. A URL optimized for search engines will be short, include hyphens, and include relevant keywords.
Hreflang Tags
Hreflang tags are HTML data that highlights the language a web page is using and the geographical restrictions the webmaster wishes to impose on that page. It helps search engines index pages correctly so that it can serve pages in the correct language for search engine users in different geographical locations around the globe. It’s why you see websites in your own language when you search.
Indexing
Indexing is the process that search engines use to find and organize websites based on keywords and topics so that it can provide relevant resources to search engine users at high speed.
Internal Links/External Links
Internal links are hyperlinks on your web pages that direct visitors to other pages of your website. External links are hyperlinks on your web pages that direct visitors to pages on other websites.
Keywords/Search Terms
Keywords or search terms are common phrases that search engine users type into search engines to find relevant content on specific topics.
Keyword Research
Keyword research is the process of finding popular or relevant search terms to use in web content. Keyword research is the start of any SEO strategy and is also used by marketers to find out what people care about or what they are looking for.
Landing Page
Landing pages are specific web pages that are designed to promote or explain a specific campaign, product, or service a business offers. A landing page aims to persuade web visitors into completing some sort of action like purchasing a product, signing up for a mailing list, or scheduling a consultation call.
Link Juice
Link Juice is a colloquial term that refers to how much ranking power a website can transfer to another website when it links to it. You will get the most ‘link juice’ from inbound links that come from sites with a high domain authority that also focuses on the same/similar topic or industry as you.
Long tail Keywords / Short tail Keywords
Short tail keywords include one or two words with general search intent. Long tail keywords are keywords that include three or more words that tend to have more specific search intent. For example, shoes would be a short tail keyword, whereas size 7 white athletic shoes would be a longtail keyword.
Metadata
Metadata provides information about other forms of data. It’s data about data! In terms of SEO search engines use metadata to understand web pages in more detail. Examples of SEO metadata include title tags, meta descriptions, alt-text, canonical tags, and header tags (H1-H6).
On-page SEO
On-page SEO describes the process of optimizing individual web pages to improve their position in the search engine results pages. It involves the optimization of both the content and the code associated with a specific web page.
Off-page SEO
Off-page SEO refers to the tactics used to boost specific web pages position in search engine results pages through external or off-site signals like backlinks and social media engagement.
Page Titles
Page titles or title tags are a form of HTML code that’s used to identify every web page on a website. Search engines show page titles on their results pages and they also show up on web browser tabs to remind users what the page was about when they move to a new tab.
PPC
PPC stands for pay-per-click and it’s a form of advertising where internet marketers pay an advertiser each time a visitor clicks on their ad. PPC advertising was first seen in 1996 and is preferred by some marketers because you only pay when you receive engagement. Google AdWords and Facebook Ads are the most used PPC platforms.
Rich Snippet
Rich snippets or special result snippets are additional information shown in search results that offers more than the information included in meta descriptions. It helps search users to find the information they are looking for without having to click through to a website.
Robots.txt
Robots.txt is a simple text file stored in a website source code that tells search engine crawlers which pages to crawl and which pages not to crawl. It’s used to prevent search engines from indexing duplicate content or private content that you don’t want showing up in search engine results pages.
Search Console
Search Console is a Google search tool that allows website owners to check and monitor indexing status and issues. You can troubleshoot SEO issues that are preventing your website from ranking better, submit sitemaps, monitor links, and more.
SERP
SERP stands for Search Engine Results Pages which describes the page that is returned to search engine users after they input a query. It includes a list of hyperlinks and meta descriptions from relevant online resources related to the searched topic or term.
SEO
SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization which is the process of adapting a website with techniques and practices that will help web pages show higher up in SERPs.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO encapsulates any technical activities carried out on a website to improve search ranking results. Technical SEO aims to help search engine crawlers find and index web pages more efficiently by providing them with the correct data and metadata.
301 Redirects
A 301 redirect is an HTML status code that signals to web browsers and search engines that a web page has permanently moved to a new URL address. 301 redirects will automatically send visitors using old URL addresses to the new one. This prevents visitors from seeing a 404 error message and prevents you from losing website visitors.
Analytics web term definitions
Understanding the website definitions of the analytical terms used to examine the data collected from your website will help you to develop effective strategies to grow your audience and business.

AB Testing
AB testing or split testing refers to the process of creating two variants of a web page and showing them simultaneously to segments of your website visitors to test the performance of each variant. A website owner can then go live or conduct further testing with the winning variant.
Alexa Rank
Alexa rank is a competitive analysis metric that measures a website’s popularity. It compares millions of websites and ranks them in order based on estimated traffic volume and visitor engagement across the previous three months.
Attribution
Attribution in web analytics refers to the process of assigning credit to a sale or conversion to a particular touchpoint along the customer’s journey. Companies may choose to credit the first click or the last click with the biggest influence on a sale. Alternatively, they might use a linear attribution model which spreads credit equally among all the customer touchpoints.
Average Order Value
Average order value is an analytical metric used to measure the average spend of all unique orders across all customers at an online store. Divide your total revenue by your total number of orders over a specific time to calculate your average order value (AOV).
Bounce Rate
Bounce rate measures how many visitors leave a site after visiting only one page. Around 40-50% is considered an average bounce rate. To calculate bounce rate, you can divide the total number of website visitors by the number of one-page visitors.
Churn
Churn is a customer retention metric that is used to measure the number of customers, users, players, or subscribers that stop using a product, service, online store, or website.
Conversion
A conversion is a moment or event where a website visitor completes a desired action like purchase a product, sign up to a mailing list, or download a podcast.
Conversion Rate
The conversion rate is the percentage of visitors that complete a desired action like completing a purchase, filling in a form, or booking an appointment. Conversion rates can be calculated by dividing the total number of conversions by the total number of web page visits or ad interactions.
CRO
CRO stands for Conversion Rate Optimization and refers to the process of enhancing or adapting a web page or advert to improve the conversion rate.
Customer Acquisition Cost
Customer acquisition cost (CAC) is the cost of gaining a new customer that completes a purchase or signs up for a service. CAC can be worked out by dividing the total cost spent on acquiring customers (marketing spend) over a given time by the total number of customers gained in the same time. So, if a business spent $1000 last month on marketing and acquired 50 customers their CAC would be $20.
Customer Lifetime Value
Customer lifetime value is the measurement of the total value a customer will bring to a business across the duration of the time that they are a paying customer. It’s a way for businesses to quantify the value of customer relationships.
Customer Retention
Customer retention refers to the ability of a company to hold on to customers after their initial purchase or sign up. If a business has high customer retention, it means they have lots of repeat purchases and their customers avoid going to a competitor.
Direct Traffic
Direct traffic is a metric used to describe web visitors that arrived without clicking a hyperlink from another site or search engine results page. Visitors may type your URL directly into the address bar, click on a saved bookmark link or click on a link from an offline application like a word doc.
Engagement Rate
Engagement rate measures the rate at which people interact with a piece of content. Interactions will vary depending on the platform the content is published on and the type of content (blog, video, image). Website engagement metrics could be time on page, new subscribers, or the number of shares a piece of content achieves.
Funnel
A funnel, sales funnel, or conversion funnel is the process or customer journey you create for website visitors that will take them through a series of steps. Starting with the first time on-site through to completing the desired conversion which could be a sale or sign up. A typical sale funnel will have four stages: Awareness > Interest > Desire > Action.
Google Analytics
Google Analytics is a tool that measures website data. It provides detailed reports on metrics like the number of users and sessions, bounce rate, average time per session, amount of return visitors, Google Ads performance, and more.
Hit
A hit describes a request to a web server for a file which indicates an interaction with your website. The file could be a web page, CCS files, Javascript, or an image. Hits differ from visits because they record every request for a particular file to be downloaded, whereas a visit just records someone or something being on the web page, no matter how many files are downloaded.
Impressions
An impression is an analytical metric used to quantify the number of views or engagements a piece of content, an advert, or a web page receives. Your web page might have been seen by lots of people but not clicked on. So, to measure that you need to collect impressions data.
Metrics
Metrics are quantitative measurements that are used to capture data of specific events, sums, or ratios. Common website analytics metrics are bounce rates, conversion rates, direct traffic, number of unique sessions, and average time on site.
Organic Search
There are two types of search results displayed on SERPs. Organic search results and paid-for search results or ads. Organic search results are pulled from the search engine index via an algorithm and they are not influenced by advertising spend. So, organic search traffic refers to the visitors on your site that have arrived from clicking the link of an organic search result.
Purchase Frequency
Purchase frequency is a metric used to measure how many times an average customer buys from a business or online store over a set time. To calculate purchase frequency you can divide the total number of orders by the total number of unique customers over the same time.
Referral Traffic
Refferal traffic is a term used to describe incoming traffic that has resulted from a visitor clicking on a hyperlink on a web page on a different domain. The linking domain refers their website traffic to you, usually because your content or product is useful to their audience in some way.
Repeat Customer Rate
Repeat customer rate measures how many customers made two or more purchases from your business or online store within a specific time frame.
Retargeting
Retargeting is the process of approaching customers, website visitors, or any other user who has previously engaged with your business or website in the past with adverts, emails, or other various call-to-actions.
Sessions
A session in web analytics refers to a group of actions carried out by a visitor within a given timeframe (usually 30 minutes).
Time on Site
Time on site is a measurement of how long website visitors have spent browsing a website, usually measured in minutes or seconds.
Touchpoints
Touchpoints are interactions with customers that can happen both online and offline. It describes the moments of contact that your customers have with your business or website before, during, and after they engage with your business in some way.
Tracking URL
A tracking or tracker URL will gather data on users that click on the link based on information from their IP addresses. Tracking URLs help web marketer understand where their traffic is coming from (direct, search or referral).
Traffic
Traffic or website traffic is simply the measurement of the number of users visiting a specific website.
Traffic Sources
Sources or traffic sources is an analytics metric used to segment the different types of traffic coming into your website. The three main sources of website traffic are Direct, Referral and Search.
Unique Visitors
Unique visitors refer to the number of individual visitors coming to your site which is measured by counting the number of unique IP addresses that visit your site. This helps web marketers distinguish between repeat visitors and one-time visitors.
Written By

Cheapest Website Builder 2021
Building a website doesn’t have to cost the earth. We’ve pulled together a list of the cheapest website builders and ecommerce platforms to help you find an affordable option for your website. Not only are they the cheapest, but some of them are the best of the best…

Web Design Trends 2021
Discover the biggest trends in web design that will emerge online throughout 2021. 3D & VR, Personalization, Parallax animations and more…
